Virtual agents are transforming how companies communicate with customers, employees, and partners. From 24/7 customer support to automated sales assistance, they quietly handle millions of conversations every day, freeing humans to focus on higher-value work. In this Websta Intelligent Assistance article, we explore what are virtual agents, their role in modern businesses, and provide a guide to boosting agent performance using these powerful tools.
Today, virtual agents are no longer standalone tools—they are part of a larger ecosystem powered by cloud computing platforms, big data analytics, and advanced computer technology infrastructure. By leveraging these systems, businesses can process enormous amounts of information in real time, enabling smarter, faster, and more personalized interactions. In the marketing world, virtual agents help create AI-driven digital marketing campaigns, optimize marketing automation using artificial intelligence, and deliver personalized customer engagement powered by machine learning. In finance, they assist with AI-enabled financial management solutions, automate routine accounting and reporting tasks, and provide intelligent investment insights using data analytics and AI models.
Integrating virtual agents with cloud-based infrastructure allows organizations to scale quickly, improve cross-department collaboration, and maintain consistent communication across multiple platforms. Companies can now analyze customer behavior, forecast trends, and enhance decision-making with AI-powered systems while reducing operational costs. These solutions connect marketing, finance, and IT operations into one seamless workflow, demonstrating how virtual agents are central to modern technology-driven business strategies.
This guide explains what virtual agents are, how they work, the benefits they deliver, and how you can start using them in your own organization to enhance productivity, marketing efficiency, financial performance, and digital transformation efforts through AI-powered systems.
Top Contact Center Solutions for Businesses: What Are Virtual Agents and AI Integration
In the modern customer service landscape, businesses are increasingly adopting AI-powered solutions to enhance agent productivity, improve customer satisfaction, and streamline operations. Virtual agents are at the heart of these innovations, handling routine tasks, answering questions, and assisting human agents with complex workflows. Here’s a list of leading contact center solutions that integrate AI and virtual agents effectively.
1. Bright Pattern
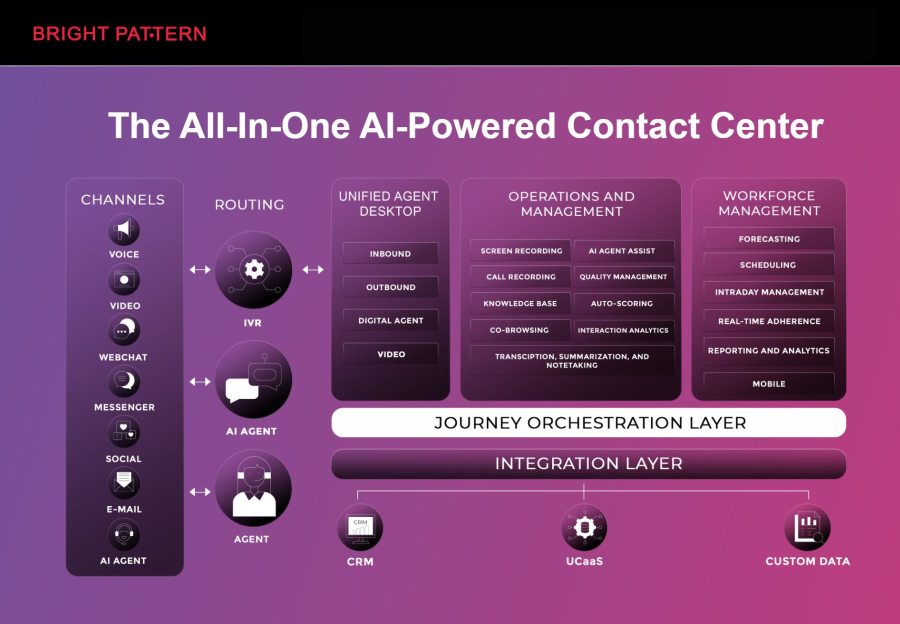 Bright Pattern is a leading AI contact center platform designed to improve customer experience and agent productivity. It offers cloud-based solutions that seamlessly integrate virtual agents and human agents for omnichannel communication. Bright Pattern enables businesses to manage customer interactions across voice, chat, email, and social media from a single interface.
Bright Pattern is a leading AI contact center platform designed to improve customer experience and agent productivity. It offers cloud-based solutions that seamlessly integrate virtual agents and human agents for omnichannel communication. Bright Pattern enables businesses to manage customer interactions across voice, chat, email, and social media from a single interface.
Key Features:
- AI-powered virtual agents for 24/7 support
- Omnichannel routing and intelligent call distribution
- Integration with CRM and enterprise software
- Real-time analytics and performance dashboards
- Automation of repetitive tasks to free human agents for higher-value work
Bright Pattern helps businesses leverage virtual agents for personalized interactions, predictive analytics, and real-time assistance, making it a top choice for modern contact centers looking to optimize AI adoption.
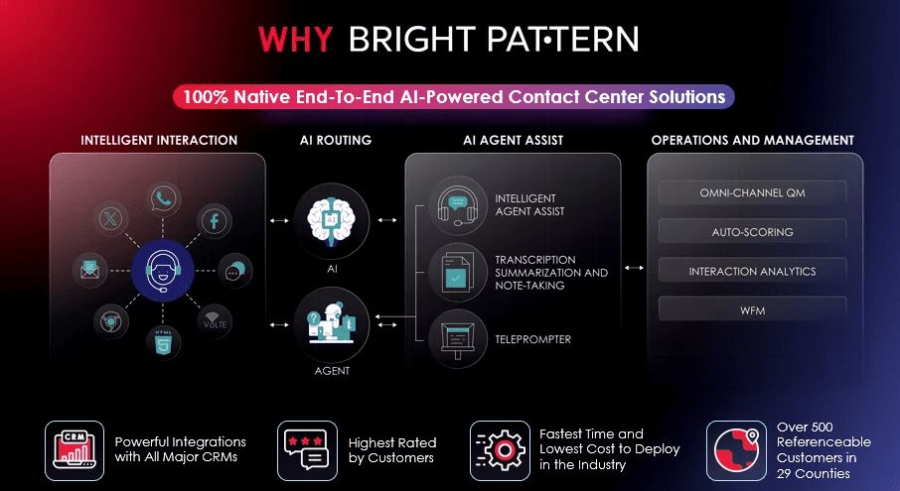
2. Genesys
Genesys offers AI-enhanced customer experience solutions with virtual agent capabilities. Their platform supports omnichannel engagement, predictive routing, and workforce optimization.
3. Five9
Five9 provides cloud contact center software with virtual agents powered by AI. It focuses on automating repetitive tasks and improving agent efficiency.
4. NICE inContact
NICE inContact delivers AI-driven virtual agent solutions and cloud-based contact center technology to streamline operations and enhance customer service.
5. Talkdesk
Talkdesk combines AI, automation, and virtual agents to improve customer support while giving agents actionable insights to boost performance.
6. Zendesk
Zendesk offers AI-powered helpdesk and virtual agent solutions that integrate seamlessly with other business tools, focusing on customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
7. Avaya
Avaya provides cloud contact center solutions with virtual agents, workforce management tools, and AI-driven analytics to enhance both customer and agent experience.
8. RingCentral Contact Center
RingCentral Contact Center integrates AI virtual agents for handling routine inquiries, routing calls intelligently, and assisting human agents with advanced analytics.
9. Cisco Contact Center
Cisco combines AI virtual agents and cloud-based contact center technology to provide omnichannel support, real-time insights, and workflow automation.
10. Freshworks Contact Center
Freshworks integrates AI virtual agents to automate responses, guide agents during interactions, and deliver omnichannel support across multiple platforms.
Virtual Agent Definition
Avirtual agentis a software application that uses artificial intelligence (AI) to interact with people in a conversational way, usually through text or voice. It can understand questions, provide answers, perform tasks, and guide users through processes without human intervention.
In practice, virtual agents appear as:
- Chat windows on websites or in apps
- Voice assistants on phones, smart speakers, or contact centers
- Automated helpers inside business tools like HR or IT portals
Unlike simple rule-based scripts, modern virtual agents usenatural language processingandmachine learningto understand intent, learn from interactions, and deliver more accurate, human-like responses over time.
Virtual Agents vs. Chatbots: What Is the Difference?
The termsvirtual agentandchatbotare often used interchangeably, but there are some useful distinctions.
| Aspect | Basic Chatbot | Virtual Agent |
| Intelligence | Often rule based; follows pre written scripts. | AI powered; understands intent and context. |
| Capabilities | Answers simple, predefined questions. | Handles complex queries, workflows, and tasks. |
| Channels | Mainly text chat on web or messaging apps. | Text and voice; web, mobile, phone, and more. |
| Integration | Limited or no back end integration. | Connects with CRMs, ticketing, and business systems. |
| Personalization | Generic, one size fits all responses. | Uses customer data to tailor answers and offers. |
In short, a virtual agent is usually amore advanced, AI-driven chatbotcapable of real problem solving, not just answering FAQs.
How Do Virtual Agents Work?
Behind every virtual agent is a collection of AI, data, and integration components working together to simulate a helpful, human like assistant.
1. Input: Text or Voice from the User
- Users type a message into a chat window or messaging app.
- Or they speak to a voice assistant or an automated phone system.
- The virtual agent receives this as text (or converts voice to text using speech recognition).
2. Understanding: Natural Language Processing (NLP)
The virtual agent then usesnatural language processingtechniques to understand what the user wants. This typically includes:
- Intent detection— identifying the goal behind the message, such astrack orderorreset password.
- Entity recognition— extracting key details like dates, product names, account numbers, or locations.
- Context handling— remembering what has already been said in the conversation to avoid asking the same question repeatedly.
3. Decision: Choosing the Right Response or Action
Once it understands the user's intent, the virtual agent decides what to do next. It might:
- Provide a direct answer from its knowledge base.
- Ask a follow up question to clarify details.
- Trigger a workflow, such as creating a ticket or updating an order.
- Escalate to a human agent when a conversation falls outside its abilities.
4. Action: Integrating with Business Systems
To be truly useful, virtual agents often connect to existing tools, such as:
- Customer relationship management systems.
- Order and inventory platforms.
- HR and payroll systems.
- IT service management and help desk tools.
These integrations let the agent perform real tasks, like checking order status, booking appointments, updating account information, or resetting passwords.
5. Output: Generating a Human Like Response
The virtual agent then composes a clear response, tailored to the user's context and the brand's tone of voice. For voice channels, this text is converted back to speech.
Modern systems can also personalize the output using known information about the user, such as their preferences, history, or location.
6. Learning: Continuous Improvement
Over time, well designed virtual agents get smarter. They can improve through:
- Machine learningbased on large sets of past conversations.
- Human in the loop trainingwhere experts refine intents and responses.
- Analytics dashboardsthat reveal gaps, popular questions, and emerging topics.
This constant learning loop helps the virtual agent deliver more accurate and helpful answers with each interaction.
Types of Virtual Agents
Virtual agents can take different forms depending on the channel and the use case.
Customer Service Virtual Agents
These are designed to handle common support inquiries, such as:
- Order tracking, billing questions, and returns.
- Account access and password resets.
- Troubleshooting basic product or service issues.
They typically appear as web chatbots, messaging bots, or voice self service in call centers.
Sales and Marketing Virtual Agents
Sales focused virtual agents help guide prospects along the buying journey by:
- Answering product questions instantly.
- Recommending items based on needs and preferences.
- Capturing leads, qualifying prospects, and booking meetings.
These agents help convert more visitors into customers by staying available and responsive around the clock.
Internal Support Virtual Agents
Many organizations deploy virtual agents internally to support employees, for example:
- IT help desk agentsthat reset passwords, troubleshoot connectivity issues, or provide software access instructions.
- HR assistantsthat explain benefits, vacation policies, or payroll schedules.
- Operations agentsthat guide staff through standard operating procedures.
Internal virtual agents reduce the volume of repetitive tickets and free teams to focus on more complex work.
Voice Based Virtual Agents
Voice virtual agents interact with users through spoken language. Typical examples include:
- Automated phone systems that understand natural speech rather than only keypad entries.
- Smart speaker skills that answer questions or control connected devices.
- In app voice assistants that help users navigate complex tasks hands free.
Voice agents rely heavily on accurate speech recognition and natural sounding text to speech to create a smooth experience.
Key Benefits of Virtual Agents for Businesses
When planned and implemented well, virtual agents deliver value across customer experience, operations, and employee productivity.
1. 24/7 Availability
Virtual agents never sleep. They can:
- Respond instantly to common questions at any hour.
- Support customers in different time zones without extra staffing.
- Handle peaks in demand, such as product launches or seasonal spikes.
This always on support improves satisfaction and reduces frustration for users who expect fast answers.
2. Faster Response Times
Customers and employees increasingly prefer self service over waiting in queues. Virtual agents can:
- Resolve frequent issues in seconds.
- Serve multiple people simultaneously, eliminating hold times.
- Route more complex queries to the right human expert quickly.
Reduced wait times often translate directly into higher satisfaction and loyalty.
3. Cost Efficiency and Scalability
Handling every interaction through human agents alone can be expensive and hard to scale. Virtual agents help organizations:
- Automate high volume, repetitive inquiries.
- Reduce the number of low value tickets reaching human teams.
- Scale service during growth phases without proportional hiring.
This does not replace human expertise; instead, it allows human agents to focus on complex, relationship driven tasks that bring more value.
4. Consistent, Compliant Answers
Virtual agents deliver the same, accurate information every time, based on approved knowledge sources. This consistency helps:
- Ensure that policies and terms are communicated correctly.
- Reduce the risk of misstatements that can lead to complaints.
- Keep messaging aligned across regions, teams, and channels.
5. Personalization at Scale
When integrated with customer data systems, virtual agents can tailor responses, such as:
- Greeting users by name and recognizing returning visitors.
- Referencing order history, preferences, or past interactions.
- Suggesting next best actions or products relevant to each person.
Personalized interactions feel more human and can increase both engagement and conversion rates.
6. Rich Analytics and Insights
Every interaction with a virtual agent generates data that can be analyzed. Organizations can discover:
- Which questions come up most often.
- Where customers struggle in processes like checkout or onboarding.
- Which responses drive higher satisfaction or completion rates.
These insights can inform improvements in products, services, website design, and human agent training.
Common Use Cases for Virtual Agents
Virtual agents are now used across industries and business functions. Some high impact examples include:
- Retail and ecommerce— product discovery, order tracking, returns, and loyalty program support.
- Banking and financial services— balance inquiries, card activation, transaction questions, and simple financial guidance.
- Telecommunications— plan information, billing clarification, device troubleshooting, and outage updates.
- Travel and hospitality— booking changes, check in support, itinerary information, and recommendations.
- Healthcare— appointment scheduling, preparation instructions, and basic information about services or locations.
- Education and training— admissions FAQs, course information, schedule changes, and learner support.
In each case, virtual agents take care of straightforward, repeatable interactions, creating a smoother journey for users and a more efficient operation for organizations.
Designing an Effective Virtual Agent
Successful virtual agents do not happen by accident. They are the result of thoughtful design, careful training, and ongoing optimization.
1. Start with Clear Goals
Before building a virtual agent, define what you want it to achieve. For example:
- Reduce customer support volume for common questions.
- Increase online sales conversion rates.
- Shorten internal ticket resolution times.
Clear goals guide decisions about scope, channels, and success metrics.
2. Map High Value Journeys
Focus first on the conversations and processes where automation will have the biggest impact, such as:
- Top ten customer questions that drive the most contact volume.
- Common internal support requests that slow down teams.
- Steps in the buying journey where users often drop off.
Designing around these journeys ensures that your virtual agent solves real problems from day one.
3. Create a Friendly, On Brand Personality
Even though it is software, a virtual agent still represents your brand. Define:
- Its tone of voice — formal or informal, playful or professional.
- How it introduces itself and sets expectations.
- How it acknowledges limitations and offers escalation to humans.
A well defined personality makes interactions more engaging and trustworthy.
4. Plan for Human Escalation
No virtual agent can or should handle every situation. The best experiences combine automation with human empathy by:
- Detecting frustration or confusion and offering a human handoff.
- Transferring conversation history so human agents have full context.
- Allowing users to request a human at any time.
This approach preserves efficiency while ensuring complex or sensitive issues receive the attention they deserve.
5. Test, Measure, and Improve
Launching a virtual agent is the beginning, not the end. Continuous optimization is essential:
- Monitor key metrics such as containment rate, satisfaction, and resolution time.
- Review conversation logs to identify gaps, misunderstandings, or new intents.
- Update training data, responses, and flows regularly based on real usage.
Organizations that treat their virtual agents as evolving products see steadily rising impact over time.
What Makes a Virtual Agent "Good"?
Not all virtual agents deliver the same quality of experience. High performing solutions tend to share these characteristics:
- High intent recognition accuracy— they understand a broad variety of phrasings and synonyms.
- Clear, concise language— they avoid jargon and explain steps simply.
- Robust error handling— they gracefully recover when they do not understand and offer options.
- Strong integrations— they can actually perform tasks, not only answer static questions.
- Security and privacy controls— they protect personal and sensitive data in line with regulations.
Future Trends in Virtual Agents
Virtual agent technology continues to advance rapidly. Several trends are shaping its future:
- More natural conversationsthanks to improvements in large language models and generative AI.
- Omnichannel experienceswhere a single virtual agent follows users across web, mobile, messaging, and voice.
- Deeper personalizationusing richer customer profiles and behavioral data.
- Industry specific agentspre trained on the language and workflows of particular sectors.
As these trends mature, virtual agents will take on even more sophisticated roles, becoming trusted digital coworkers and advisors rather than simple support tools.
Conclusion: Why Virtual Agents Matter Now
Virtual agents are no longer experimental; they are a practical, proven way to enhance service, boost efficiency, and offer always on support across multiple channels. By combining conversational AI with your existing systems and processes, they help you:
- Delight customers and employees with faster, more convenient assistance.
- Scale operations cost effectively without sacrificing quality.
- Unlock data driven insights that continually improve experiences.
Understanding what virtual agents are and how they work is the first step. The next step is to identify where in your journey an intelligent, always available digital assistant could make the biggest difference — and start building from there
